Sleep is a vital part of our daily lives, yet it’s often overlooked in the hustle and bustle of modern life. For many, the focus is placed on productivity, work, and maintaining a busy schedule, while sleep tends to be seen as a luxury rather than a necessity. However, the link between sleep and physical health is profound and cannot be ignored. Understanding how quality sleep influences overall health can lead to healthier choices and better well-being.
How Sleep Affects Physical Health
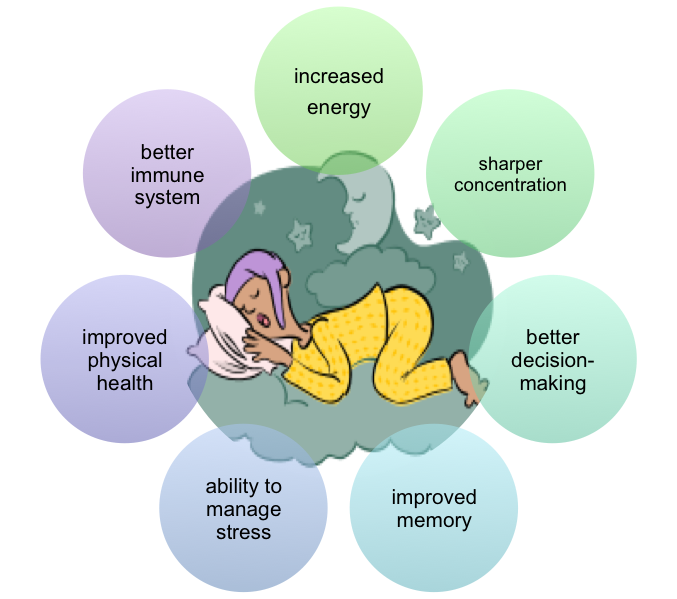
- Supports Immune Function One of the most significant benefits of sleep is its impact on the immune system. During deep sleep, the body produces cytokines, which are proteins that help combat infection, inflammation, and stress. A consistent lack of sleep can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to illnesses and slower to recover. Good sleep hygiene can lead to fewer sick days and a more resilient immune system.
- Promotes Cardiovascular Health The heart and blood vessels benefit greatly from adequate sleep. Research has shown that poor sleep quality can contribute to the development of cardiovascular conditions such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. During sleep, the body’s blood pressure decreases, giving the cardiovascular system a chance to rest. This downtime is essential for heart health, and a consistent sleep schedule can help maintain healthy blood pressure levels and reduce the risk of heart-related issues.
- Regulates Metabolism and Weight Sleep and metabolism are closely linked. Inadequate sleep can disrupt the balance of hunger-related hormones like ghrelin and leptin. Ghrelin signals hunger to the brain, while leptin helps you feel full. When you don’t get enough sleep, ghrelin levels increase, making you feel hungrier and leading to a higher likelihood of overeating. Additionally, sleep deprivation can reduce insulin sensitivity, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes. Getting enough restorative sleep can support healthy metabolism, aid in weight management, and reduce the risk of metabolic disorders.

- Aids in Muscle Repair and Growth For those who are physically active or involved in regular exercise, sleep is crucial for muscle repair and growth. During deep sleep stages, the body produces growth hormones that facilitate muscle repair and tissue growth. This is particularly important for athletes and individuals looking to build strength and recovery after workouts. Sleep supports the body’s ability to repair muscle fibers, replenish energy stores, and improve overall performance.
- Reduces the Risk of Chronic Conditions Chronic conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and hypertension have all been linked to poor sleep habits. Sleep disturbances can lead to systemic inflammation and hormonal imbalances, which contribute to the development of these health conditions over time. By prioritizing sleep, individuals can significantly lower their risk of developing chronic health issues and support the long-term health of the body.
- Enhances Brain Function and Cognitive Health While the brain might not be a physical organ in the same way as the heart or lungs, its health is deeply connected to overall physical well-being. Sleep plays a vital role in cognitive functions such as memory, problem-solving, and concentration. During sleep, the brain consolidates memories, processes information, and clears out toxins that accumulate during waking hours. A well-rested brain can improve focus, boost productivity, and support mental clarity, ultimately contributing to a higher quality of life.

Tips for Prioritizing Sleep for Better Health
- Create a Sleep Schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps regulate your body’s internal clock and improves sleep quality. Try to keep this schedule even on weekends to maintain consistency.
- Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment: Make your bedroom a comfortable and relaxing place. This means minimizing light, noise, and other distractions. Consider blackout curtains, white noise machines, or earplugs to create an optimal sleeping environment.
- Limit Screen Time Before Bed: The blue light emitted from screens can interfere with melatonin production, a hormone that signals sleep. Aim to put away phones, tablets, and computers at least an hour before bedtime.
- Stay Active During the Day: Regular physical activity can help you fall asleep faster and deepen your sleep. However, try to avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime, as it can have the opposite effect.
- Mind Your Diet: Avoid large meals, caffeine, and alcohol before bedtime. Caffeine and alcohol can disrupt sleep cycles, and large meals can lead to discomfort that hinders sleep.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Activities such as meditation, deep breathing, or gentle stretching can help relax the body and mind before bed.
Conclusion
Sleep is far more than just a period of rest; it’s an essential component of physical health and well-being. By prioritizing quality sleep, individuals can support their immune system, cardiovascular health, metabolism, and brain function, all while reducing the risk of chronic health conditions. Understanding the profound connection between sleep and health is the first step in making conscious efforts to improve sleep habits. With these changes, it’s possible to transform not just the way you feel during the day, but your overall health for years to come.

